Calculation of Beta
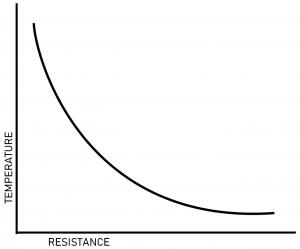
A thermistor’s “b” value, or beta value, is an indication of the shape of the curve representing the relationship between resistance and temperature of an NTC thermistor. Calculating the beta value is a vital step in the component selection process as it gives the characteristic at a given temperature vs the resistance for a specific application.
Beta Value and NTC Thermistors
NTC thermistors are non-linear resistors that alter their resistance characteristics with temperature. Simply put, as temperature increases the thermistor’s resistance decreases. The manner in which the resistance of a thermistor decreases is related to a constant known in the thermistor industry as beta (β).
Beta is measured in degrees Kelvin (K) and is computed based on the formulation given below.
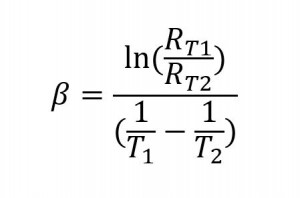
Where:
Rt1 = Resistance at Temperature 1
Rt2 = Resistance at Temperature 2
T1 = Temperature 1 (K)
T2= Temperature 2 in (K)
A more accurate method is to use the Steinhart and Hart method, which uses three temperatures over a given range.
For more information, see our blog post on The Secret to Successful Thermistor Beta Calculations.




